Describe the Structure of the Cytoskeleton.
The strength and the type of these adhesions are pivotal for regulating the assemblydisassembly of the cytoskeleton components. Describe distinguishing characteristics of the structure and growth of fungi ameba alveolates and trypanosomes.

What Is The Cytoskeleton Mbinfo
Differ in size and each carries out specific functions within the cell.

. The membrane-enclosed organelles discussed in the preceding chapters constitute one level of the organizational substructure of eukaryotic cells. 1 The cytoskeleton of a cell is made up of microtubules actin filaments and intermediate filaments. The cytoskeleton supports the cell gives it shape organizes and tethers the.
Describe the structure and function of myosin II myosin I V VI. Plant and Animal Cells -Describe the structure and function of the ribosomes. It is made of protein and it maintains the cell shape protects the cell and enables every cell to move freely using some specific structures such as flagella and cilia.
Located in the cytosol. They function in cellular movement have a diameter of about 7 nm and consist of two intertwined strands of a globular protein we refer to as actin see image belowFor this reason we refer to microfilaments as actin filaments. Want to see the full answer.
The cytoskeleton structure is modified by adhesion to neighboring cells or to the extracellular matrix ECM. Intermediate filaments which serve to support the cell itself rapidly which serve to support the nucleus and plasma. Despite differences in structure and function all living cells in multicellular organisms are surrounded by a cell membrane.
Each centriole is a cylinder of nine triplets of microtubules. Microtubules intermediate filaments and microfilaments. It contains a pair of centrioles two structures that lie perpendicular to each other.
The cytoskeleton gives cells structure and shape and allows them to move around. This dynamic property enables cellular movement which is governed by forces both internal and external. Science Biology QA Library Describe the location structure and function of eukaryotic cell organelles and cytoskeleton and compare and contrast bacterial and eukaryotic cell structure.
Rapidly microtubules The cytoskeleton is made of three types of protein fibers. Microtubules are the largest element of the cytoskeleton. Often referred to as the bones and muscles of an animal cell the cytoskeleton functions in support such as vesicle transport of materials and movement determining a cells shape.
It is found in all cells though the proteins that it is made of vary between organisms. Microtubules along with microfilaments and intermediate filaments come under the class of organelles known as the cytoskeleton. In eukaryotes it is composed of three main components microfilaments intermediate filaments and.
Made of proteins and RNA. Myosin II light chains and actin binding domain for muscle contraction and cell movements myosin I V VI all involved in membrane attachment for vesicle trafficking. The cytoskeleton has three different types of protein elements.
1 Continued synaptic receptors eg AMPA receptor and channels activation during memory maintenance in the memory spines to regulate molecules that control actin dynamics and branching. They provide rigidity and shape to the cell and facilitate cellular movements. The cytoskeleton organizes other constituents of the cell maintains the cells shape and is responsible for the locomotion of the cell itself and the movement of the various organelles within it.
A further level of organization is provided by the cytoskeleton which consists of a network of protein filaments extending throughout the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. Microfilaments are often associated with myosin. The cytoskeleton doesnt have bones per se but it does have three main components.
Network of long protein strands. It extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. 2Microtubules are microscopic hollow tubes made of alpha and beta tubulin that are a part of the cells cytoskeleton.
Dynamic structure composed of microtubules microfilaments and intermediate filaments which are capable of rapid assembly or disassembly dependent on the cells requirements. 1Describe the cytoskeleton function in cell movement. Microtubules There are 206 bones in the human body.
Functions in maintaining cell shape intracellular movement migration of cells cell division formation of specialized structures. This actin cytoskeleton structure lasts beyond actin and its regulatory proteins turnover and dynamics by several molecular activities see numbers in figure. Cytoskeleton a system of filaments or fibres that is present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells cells containing a nucleus.
2What is the Endomembrane System. The cytosol of cells contains fibers that help to maintain cell shape and mobility and that probably provide anchoring points for the other cellular structures. The cytoskeleton is a kind of temporary structure present in all the cells within any living organism.
Describe the structure and function of mitochondria and peroxisomes Explain the three components of the cytoskeleton including their composition and functions Now that you have learned that the cell membrane surrounds all cells you can dive inside of a prototypical human cell to learn about its internal components and their functions. -Describe the structure and function of the cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton is the framework of the cell which forms the structural supporting component.
Collectively these fibers are termed as the cytoskeleton. The cytoskeletal elements are composed of different proteins. Just like the outer layer of the skin separates the.
The cytoskeleton is a complex dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells excluding bacteria and archaea. From narrowest to widest they are the microfilaments actin filaments intermediate filaments and microtubules. The cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules that extends throughout a cell through the cytoplasm which is all of the material within a cell except for the nucleus.
The cytoskeleton of most eukaryotic cells is composed of three basic structural components collectively called cytoskeletal elements. As their name implies microtubules are small hollow tubes. The filaments that comprise the cytoskeleton are.
Helps with movement of organelles in the cytosol. It helps transport inside the cytoplasm like the movement of vesicles and organelles for example and it helps in. The cytoskeleton provides a structural framework for the cell.
Of the three types of protein fibers in the cytoskeleton microfilaments are the narrowest. Check out a sample QA here. The centrosome replicates itself before a cell divides and the centrioles play a role in pulling the duplicated chromosomes to opposite ends of.
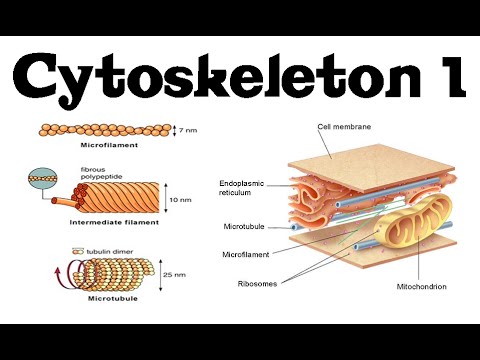
Cytoskeleton Structure And Function 1 Actin Microtubules And Intermediate Filaments Youtube

The Cytoskeleton Flagella And Cilia And The Plasma Membrane Biology For Non Majors I

Cytoskeleton Structure Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Comments
Post a Comment